Can Anti-Anxiety Medications Help with Weight Loss?
Anxiety is a pervasive issue in today’s fast-paced world, affecting millions of individuals worldwide. The increasing pressures of work, relationships, and social expectations have led to a surge in cases of anxiety disorders. To manage these symptoms, many turn to anti-anxiety medications, which have proven to be effective for mental health management. However, an intriguing aspect of these medications is their potential impact on weight. Some individuals report weight loss as a side effect, while others experience weight gain. This article explores the relationship between anti-anxiety medications and weight, delving into their mechanisms, effects, and real-life experiences.

What Are Anti-Anxiety Medications?
Anti-anxiety medications are specifically designed to alleviate symptoms of anxiety by targeting neurotransmitters in the brain. These neurotransmitters, such as serotonin, dopamine, and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), play crucial roles in regulating mood, stress, and overall emotional well-being. The most commonly prescribed types of anti-anxiety medications include:
Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs): These medications, such as Fluoxetine and Paroxetine, work by increasing serotonin levels in the brain. Serotonin helps stabilize mood and reduce feelings of anxiety.
Benzodiazepines: Medications like Lorazepam and Diazepam act as sedatives by enhancing the calming effects of GABA. They are typically prescribed for short-term or acute anxiety relief.
Serotonin-Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors (SNRIs): Drugs like Venlafaxine and Duloxetine increase both serotonin and norepinephrine, which can improve mood and reduce anxiety.
Atypical Antidepressants: Bupropion, while primarily used for depression, is often prescribed off-label for anxiety and is known to have weight-related effects.
How Do Anti-Anxiety Medications Affect Weight?
The relationship between anti-anxiety medications and weight is complex and varies depending on the medication, individual physiology, and lifestyle factors. While some medications may lead to weight gain, others are associated with weight loss. Understanding these effects can help individuals and healthcare providers make informed decisions.
Weight Gain
Some anti-anxiety medications, particularly SSRIs like Paroxetine, are associated with weight gain. Reasons for this include:
Increased Appetite: As anxiety symptoms diminish, individuals may feel more relaxed and enjoy food more, leading to an increase in caloric intake.
Metabolic Changes: Certain medications can slow metabolism, making it easier to gain weight even with the same level of food consumption.
Behavioral Factors: Reduced anxiety can sometimes result in decreased physical activity, contributing to weight gain.
Weight Loss
Conversely, other medications, such as Venlafaxine (an SNRI) and Bupropion, are more likely to cause weight loss. Potential reasons include:
Appetite Suppression: These medications may reduce hunger cues, leading to lower food consumption.
Increased Energy Levels: Some medications enhance energy and motivation, prompting individuals to adopt a more active lifestyle.
Side Effects: Nausea and gastrointestinal discomfort, common with some medications, may reduce food intake temporarily.
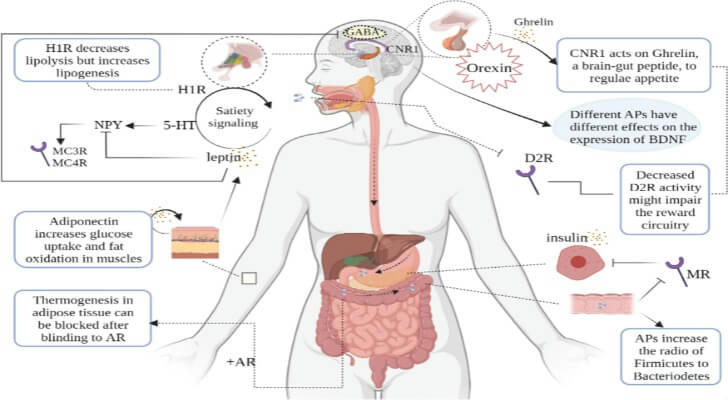
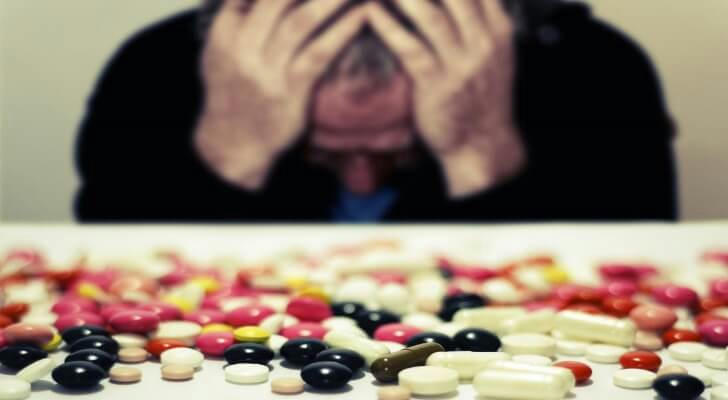
Why Do These Changes Happen?
Weight fluctuations while on anti-anxiety medications can be influenced by a combination of biological and behavioral factors. These include:
Neurotransmitter Regulation: Changes in serotonin and norepinephrine levels can alter appetite and energy balance.
Metabolic Impact: Some medications may influence metabolic rate, either speeding it up or slowing it down.
Behavioral Shifts: As anxiety improves, individuals may adopt healthier or, in some cases, less healthy habits, such as changes in diet or physical activity.
Research on Anti-Anxiety Medications and Weight
Scientific studies have examined the link between anti-anxiety medications and weight changes:
Short-Term Effects: In the initial months, medications like Fluoxetine are often associated with weight loss due to side effects like nausea or appetite suppression.
Long-Term Effects: Over time, the body adjusts to the medication, and weight may stabilize or even rebound. For example, individuals who initially lose weight on Fluoxetine may regain it as their appetite normalizes.
Medication-Specific Findings: Research has shown that Venlafaxine and Bupropion are more likely to cause weight loss, while Paroxetine tends to lead to weight gain.
Real-Life Case Examples
Case 1: Emily’s Journey with Venlafaxine
Emily, a 32-year-old teacher, struggled with chronic anxiety that disrupted her daily life. After starting Venlafaxine, she noticed a decrease in her appetite and lost 12 pounds over three months. Additionally, she felt more energetic and began incorporating hiking into her weekends. Over a year, Emily maintained her weight loss and experienced significant improvements in her mental health.
Case 2: Tom’s Experience with Paroxetine
Tom, a 45-year-old project manager, turned to Paroxetine for anxiety relief. While his anxiety symptoms improved, he began craving sugary snacks and gained 18 pounds within six months. Realizing this trend, Tom consulted his doctor, who adjusted his treatment plan. Tom’s experience highlights the potential for weight gain with certain medications and the importance of monitoring changes.
Case 3: Sarah’s Challenge with Fluoxetine
Sarah, a 28-year-old graphic designer, started Fluoxetine to manage her anxiety and depression. She initially lost 8 pounds due to appetite suppression but regained the weight after six months as her body adapted. Sarah’s case underscores the temporary nature of weight loss with some medications.
Case 4: James’ Success with Bupropion
James, a 38-year-old marketing professional, found success with Bupropion. Unlike other medications he had tried, Bupropion helped improve his mood without increasing his appetite. Over six months, he lost 15 pounds and felt more motivated to exercise. James’ case demonstrates the potential for weight loss with specific medications.

Practical Advice for Managing Weight
If you are concerned about weight changes while taking anti-anxiety medications, consider the following tips:
Monitor Your Weight: Regularly track your weight to identify any significant changes early on.
Adopt Healthy Habits: Incorporate balanced meals, regular physical activity, and stress management techniques into your routine.
Communicate with Your Doctor: Keep an open dialogue with your healthcare provider to adjust medications or treatment plans as needed.
A Holistic Approach to Mental and Physical Health
Managing anxiety effectively requires a comprehensive approach that combines medication with lifestyle changes. While medications can play a critical role in improving mental health, factors like diet, exercise, and therapy are equally important for overall well-being. By adopting a holistic strategy, individuals can achieve better mental health and maintain a healthy weight.
This exploration of anti-anxiety medications and weight demonstrates that while some medications may lead to weight loss, this effect is not universal. Each person’s experience is unique, and the decision to use medication should always be guided by medical advice and a focus on overall health.